CURRENT ISSUE
EDITOR'S PICKS
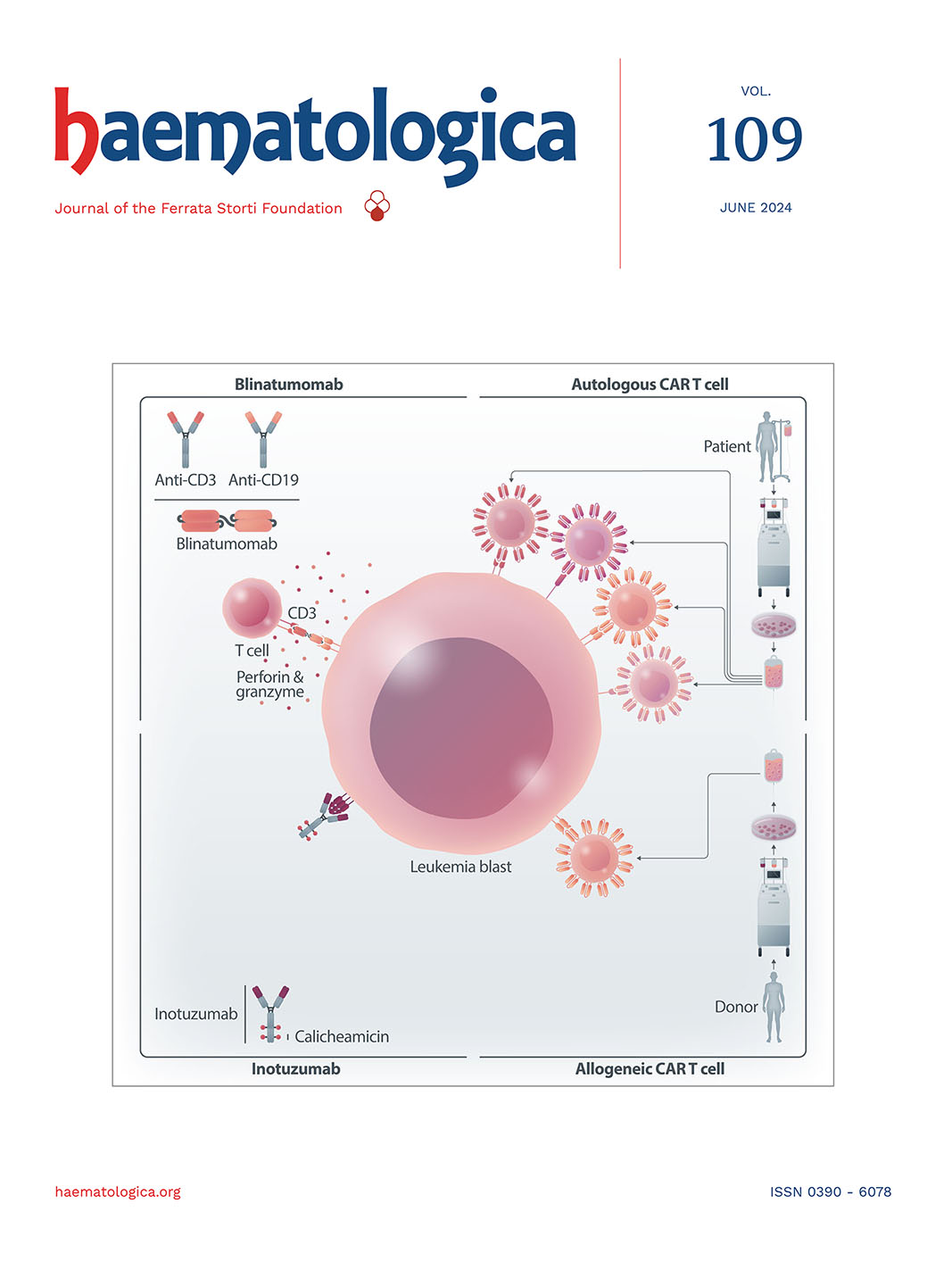
Review Series on Immunotherapy for Childhood Malignancies
Introduction. Immunotherapy for childhood malignancies: the future is now
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in childhood acute myeloid leukemia: how far are we from a clinical application?
Bispecific T-cell engagers in childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Chimeric antigen receptor therapy for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: finally catching up with B-cell leukemia?
Allogeneic chimeric antigen receptor T cells for children with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Naked antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates: targeted therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Letter
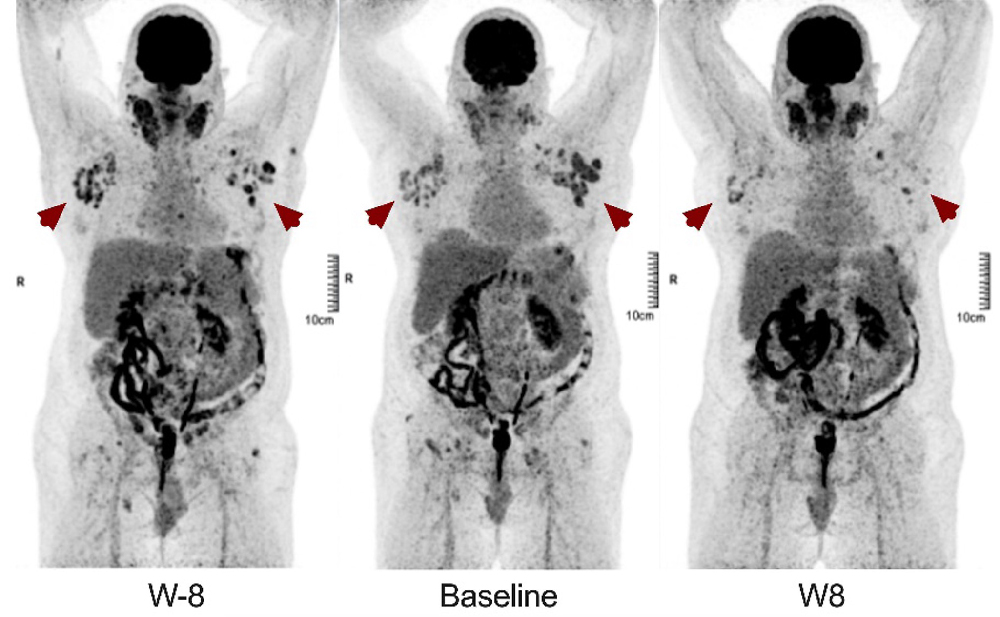
Targeting CCR4 with mogamulizumab in refractory CD3-CD4+ lymphocytic-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome
Lymphocytic-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome (L-HES) is an indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by chronic peripheral blood hypereosinophilia and eosinophil-related organ damage. Mogamulizumab is a defucosylated monoclonal antibody targeting CCR4+ cells through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Here, Ledoult and colleagues report on the very first case series of L-HES patients with severe multi-refractory-treatment disease treated with off-label mogamulizumab.
Letter
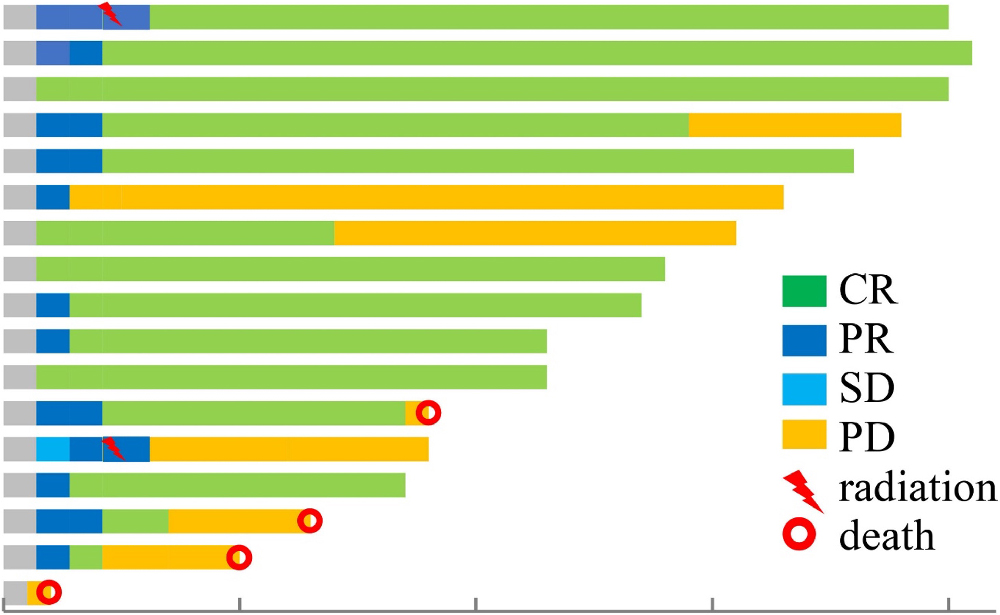
Lenalidomide, rituximab, and methotrexate are effective in newly diagnosed primary central nervous system lymphoma
The majority of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) are ineligible for autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation because they are not fit enough to undergo the procedure or they are elderly; thus, an effective and well-tolerated treatment option for these patients is needed. Yuan and colleagues present results from the multicenter, single-arm, open-labeled, phase II clinical trial of combined lenalidomide, rituximab, and methotrexate (R2-MTX) in newly diagnosed PCNSL. The R2-MTX regimen appears to be effective and well-tolerated in newly diagnosed transplant-ineligible PCNSL, especially in patients in the low-to-intermediate IELSG risk group.
Letter
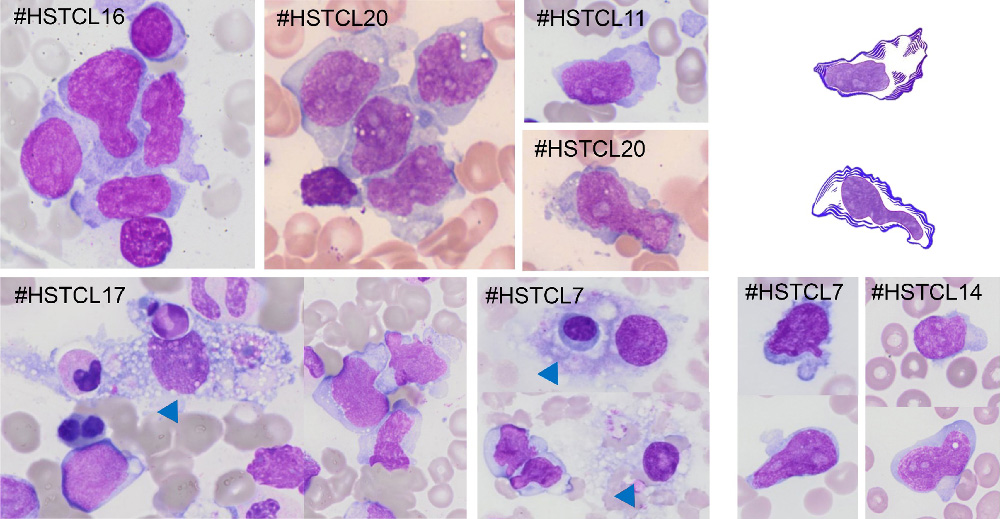
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma displays an original oyster-shell cytological pattern and a genomic profile distinct from that of γδ T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) arises from the proliferation of gamma/delta T cells (γδT), and large granular lymphocytic leukemia (LGLL) arises from proliferation of cytotoxic alpha/beta T cells, although sometimes, LGLL can carry a γδT-cell receptor. Desmares and colleagues conducted a study aimed to establish novel diagnostic criteria for distinguishing HSTCL from γδT-LGLL by combining morphology, cytogenetics and targeted sequencing. This comprehensive characterization highlights a specific oyster-shell morphology and restricted TRG and TRD segment usages in HSTCL, providing a valuable tool for distinguishing HSTCL from other γδT proliferations.
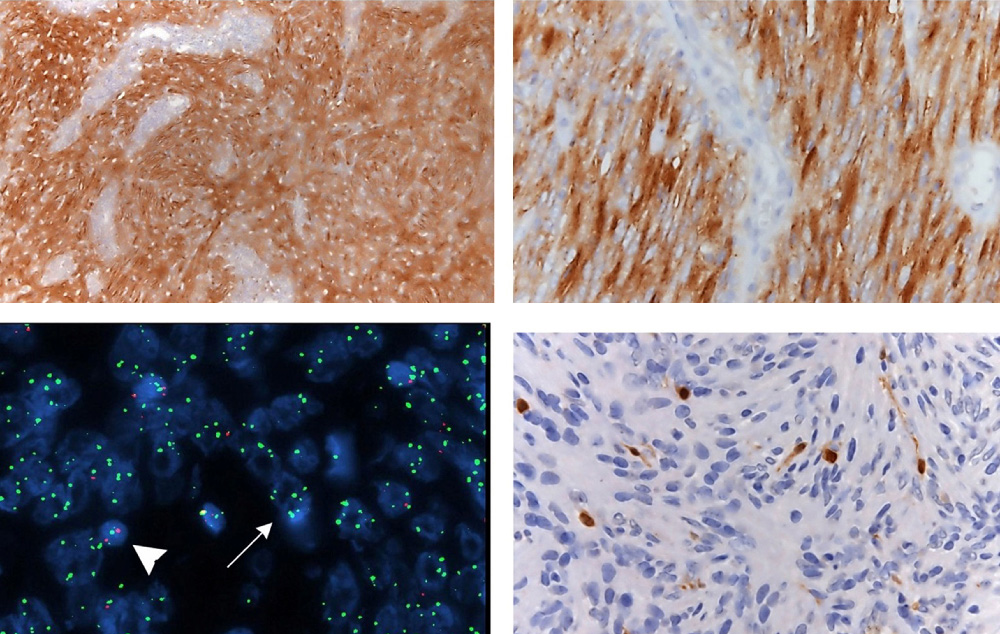
Article
Massive parallel sequencing unveils homologous recombination deficiency in follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (FDCS) is a malignant neoplasm of mesenchymal derivation included in the chapter of “Stroma-derived neoplasms of lymphoid tissues” in the 5th edition of the WHO classification. Using massive parallel sequencing, Lorenzi and colleagues analyzed a large cohort of this rare disease. This study provides a deep insight into what we know about the pathobiological mechanisms of FDCS and the identification of novel markers of potential therapeutic significance.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA